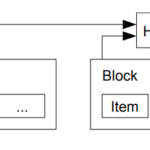
Satoshi White Paper #7. Reclaiming Disk Space explained.
This allows old blocks to be compacted by cutting off branches of the tree, and the interior hashes don't need to be stored.
Satoshi White Paper #6. Incentive explained.
This reward is like gold miners using resources to add gold to circulation, but in this case, it's CPU time and electricity being used.
Satoshi White Paper #5. Network explained.
In this way, a chain of blocks is created, with each block representing a set of transactions that have been verified and accepted by the network.
Satoshi White Paper #4. Proof of Work explained.
Once the work is done, the block cannot be changed without redoing the work, which makes the system secure.
Satoshi White Paper #3. Timestamp Server explained.
Each timestamp also includes the previous one, forming a chain that becomes stronger with each new addition.
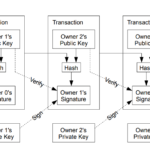
Satoshi White Paper #2. Transactions explained.
One solution is to have a trusted central authority, called a mint, that checks every transaction to make sure no one is double-spending. But this means every transaction has to…
Satoshi White Paper #1. Introduction explained
transactions would be verified using a secure computer system
Satoshi White Paper Abstract paragraph explained.
Digital signatures can help with this, but the problem of double-spending still exists, which means spending the same money twice
Taxpayers here down €1.25bn as fears over Credit Suisse hits banks
plunging share prices push hopes of recovery on the State's crash-era stakes
Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System
We propose a solution to the double-spending problem using a peer-to-peer network.